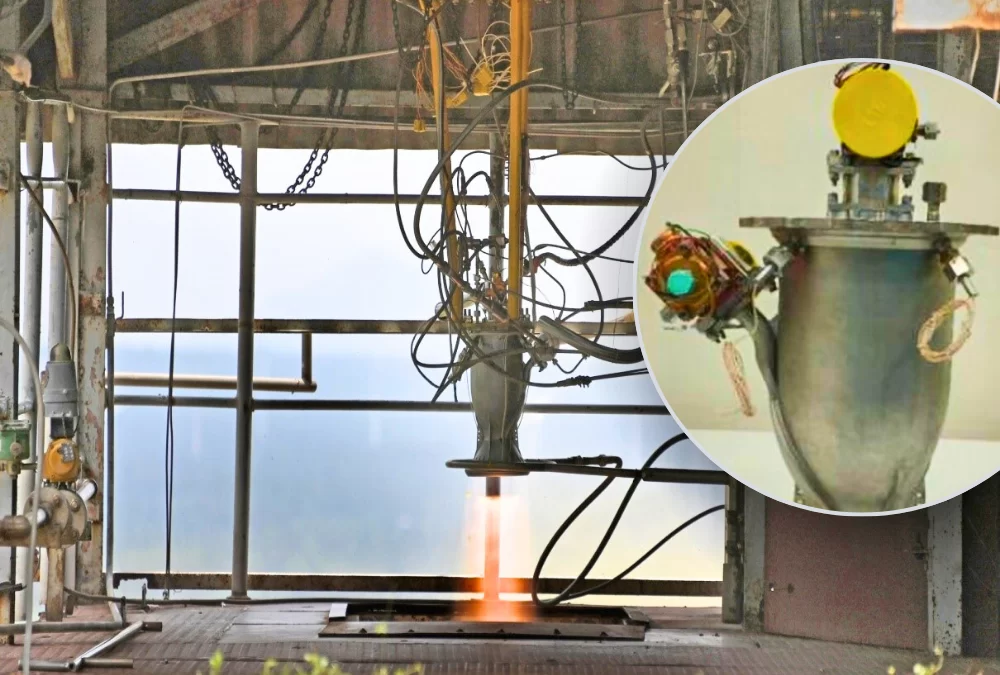
In a significant development for India’s space program, the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) successfully test-fired a liquid rocket engine built using 3D printing technology on May 9, 2024. This marks a major breakthrough that could enhance India’s capabilities and ambitions in space exploration.
The engine, designed for the upper stage of the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV), is a modified version of the PS4 engine. ISRO redesigned the engine specifically for additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing. This innovative approach offers several advantages over traditional manufacturing techniques.
Benefits of 3D-Printed Rocket Engines:
Reduced Complexity: 3D printing allows for the creation of a single, complex component, eliminating the need for multiple parts and the associated weld joints (ISRO reduced the number of parts from 14 to 1). This simplification improves engine reliability and reduces the risk of failure.
Material Efficiency: The 3D printing process uses significantly less raw material compared to conventional methods. ISRO reports a 97% reduction in material waste, with the new engine requiring only 13.7 kilograms of metal powder compared to the 565 kilograms needed for traditional manufacturing.
Faster Production: 3D printing streamlines the production process, leading to a 60% reduction in overall production time. This allows ISRO to manufacture engines faster and potentially increase launch frequency.
ISRO’s Achievement and Future Implications:
The successful test firing of the 3D-printed engine represents a significant milestone for ISRO. It demonstrates the organization’s ability to leverage cutting-edge technologies to improve its space vehicles. This technology has the potential to revolutionize India’s space program by:
Reducing Launch Costs: The efficiency gains from 3D printing can lead to significant cost savings in engine production, ultimately reducing the overall cost of launches.
Enabling New Designs: 3D printing allows for the creation of complex geometries that are difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional methods. This opens doors for the development of more advanced and efficient rocket engines.
Boosting Launch Capabilities: Faster production times and potentially lower costs could enable ISRO to increase its launch capabilities, allowing for more frequent missions and satellite deployments.
The successful test is a major step forward for India’s space ambitions. By embracing 3D printing technology, ISRO is positioning itself for a more robust and cost-effective space program in the years to come.